The field of Diagnostic Medical Radiology, also called Radiologic Technologist, is divided into several different specialties. Each specialty focuses on a different area of the body, and thus involves slightly different procedures and training.
All of these specialties are common enough to be taught in a traditional Radiologic tech school or training program, and any of them can be performed on patients of any age with the same level of risk. Here is a quick look at the different specialties of medical Radiology.
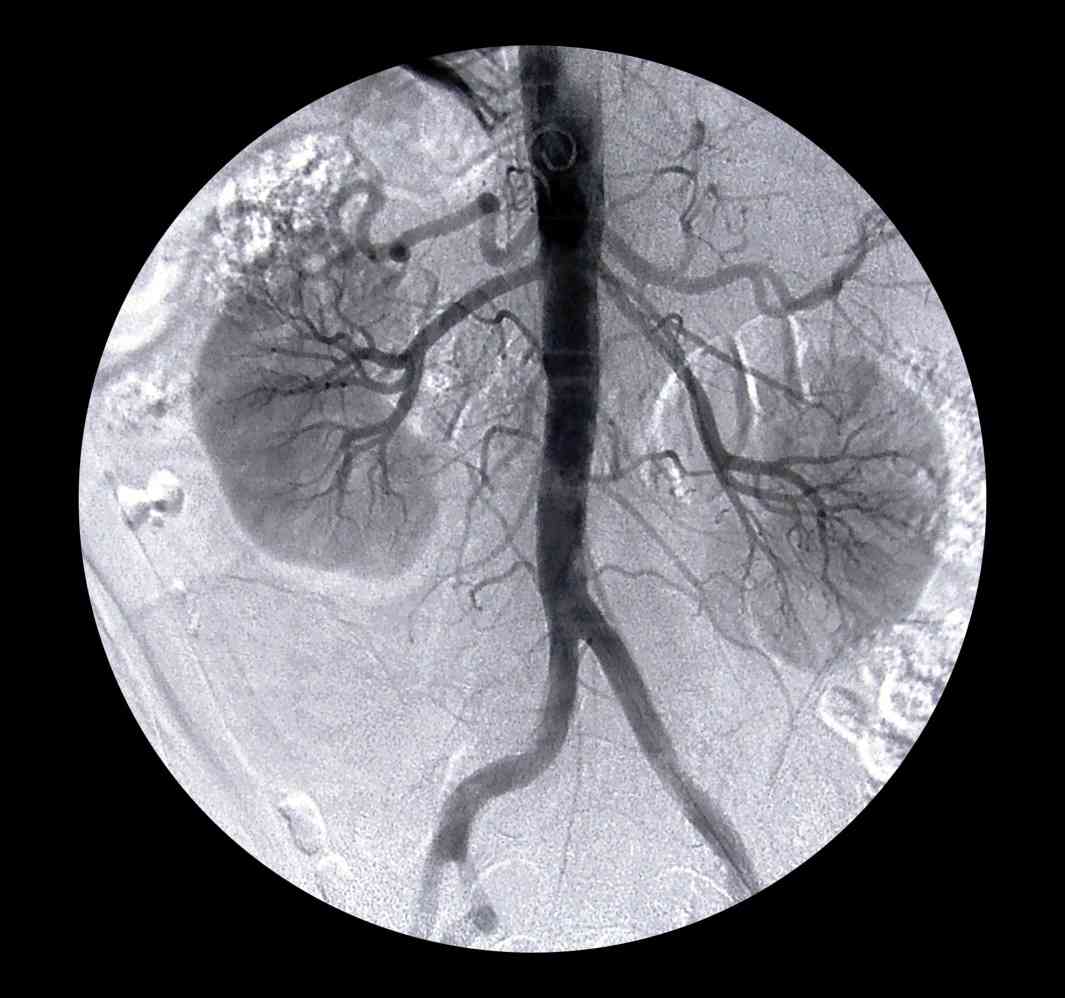
Abdominal Radiologic
Radiologic Technologist in abdominal Radiology are primarily concerned with detecting and diagnosing problems concerning the kidneys, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, spleen and male reproductive system.
This area of Radiologic is useful in the case of inflamed or enlarged abdominal organs, gall stones or bladder stones, or an aneurysm in the abdominal aorta. Abdominal Radiology may also use Doppler Radiologic to monitor blood flow as they guide a needle during needle biopsies.
Abdominal Radiologic may be limited by certain factors, however. For example, Radiologic does not pass through air or gas, so the presence of intestinal gas will block Radiologic scans. It is also less effective on large or obese patients, as the strength of the Radiologic beam weakens as it passes through more tissue.
Breast Radiologic
Breast Radiology is used primarily to investigate breast abnormalities detected by a physician during a physical exam, or during a mammography. Breast Radiologic can determine whether an abnormality is solid or fluid, which can suggest it is either a tumor that may be cancerous, or a benign cyst.
In the event that an Radiologic scan cannot determine the nature of a breast abnormality, it can be used to assist in a biopsy, whereby cells can be removed from the abnormality and examined under a microscope. This procedure is much more effective in identifying a breast abnormality, though it is more invasive than a simple Radiologic scan.
Cardiac Radiologic (Echocardiography)
Cardiac Radiologic procedures, also called echocardiograms, involve using Radiologic to scan a patient’s heart. This procedure gives the examiner an accurate means of monitoring blood flow and heart activity, as well as the health of the heart valves and muscle tissue, using a real-time, moving image.
Cardiac Radiology is commonly used by pediatric doctors to rule out heart problems in young children, or to monitor a heart problem if one has been discovered.
Echocardiographers use cardiac Doppler Radiologic to produce a moving image of the patient’s blood flow. This allows the technician to observe the speed and direction of blood flow and the functioning of the heart valves. Color flow mapping is sometimes used in conjunction with cardiac Doppler to render the image in color, allowing the physician to more easily spot abnormalities.
Neuroradiology
NeuroRadiology use Radiologic to diagnose problems with the central nervous system, including the brain.
By examining the blood vessels in the brain and nervous system, Radiologic Technologist in neuroradiology can confirm a stroke or brain aneurysm. The procedure can also be used during neonatal care to monitor nervous system abnormalities in premature infants, and to check for signs of a stroke in infants diagnosed with sickle-cell anemia.
Obstetric / Gynecologic Radiologic
Fetal imaging is the most common use of Radiologic in the medical field, and is the primary focus of obstetric radiology. In obstetric and gynecologic radiology, Radiologic is used to observe and monitor the fetus during prenatal care. This imaging technique can determine the sex of the unborn baby, as well as track its growth and progress through development.
Gynecologic radiology can also be used to determine whether a fetus is showing signs of birth defects. However, results in this area can be misleading, and false positives and false negatives are a possibility. (See more info on prenatal Radiologic.)
Vascular Radiologic
Vascular radiology procedures are used to study the body’s complex system of veins and arteries.
Radiologic can be used in these cases to detect conditions such as blocked or damaged arteries. Using Doppler Radiologic Technologist can monitor blood flow and spot areas of damage or blockage.
Blockage can occur due to blood clots, emboli, plaque or other bloodstream abnormalities, and shows up in an Radiologic scan as a disruption in blood flow. This process can be used to determine the risks involved in other procedures, such as surgery to open or bypass blood vessels.
More Information: